|
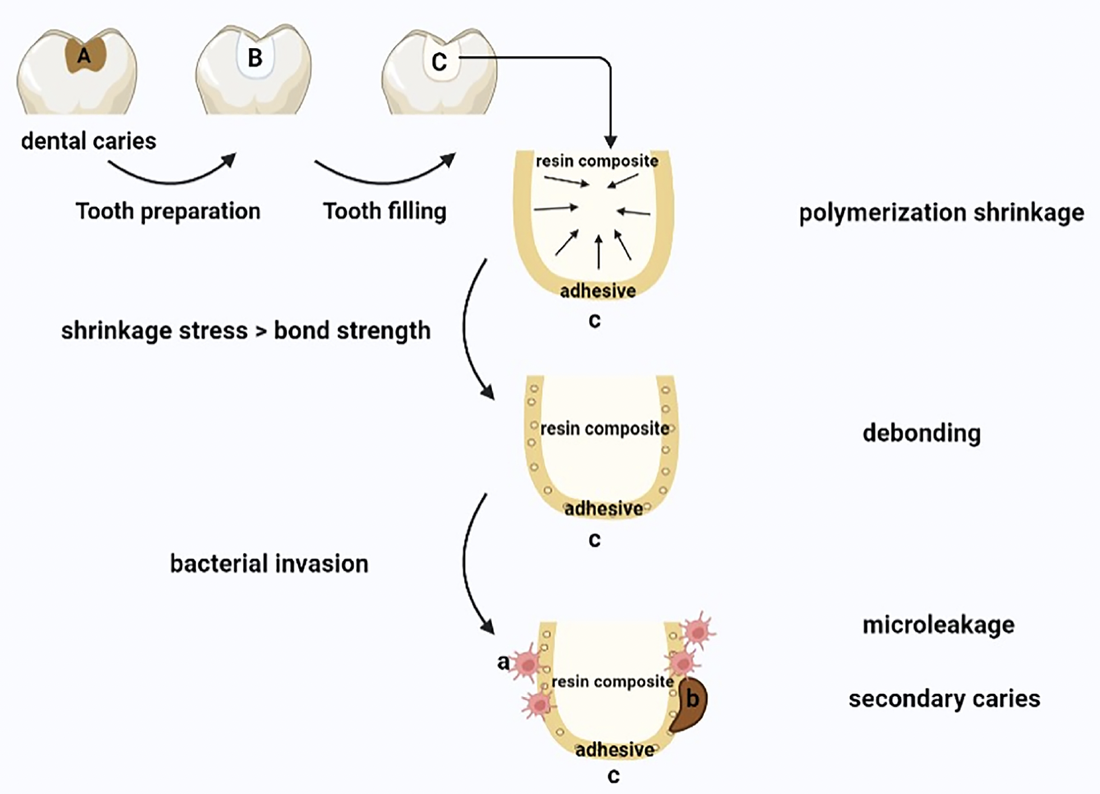
The configuration factor (C-factor) is an index used to evaluate the relationship between cavity configuration and the development of polymerization shrinkage stress in dental restorations. Although C-factor has been widely researched, its correlation with stress analysis in dental restorations remains controversial. This review aims to discuss the application and limitations of C-factor and define the restricted conditions under which the C-factor “rule of thumb” is applicable.The C-factor alone cannot provide an accurate prediction of the shrinkage stress of restorations and the mechanical behavior of material-tooth interfaces. C-factor is only applicable under one condition not typically seen in clinical practice: low, near-rigid compliance. Conditions for the application of C-factor have been explicitly defined. A more accurate and precise understanding and utilization of the C-factor is of benefit as it contributes to better understanding of polymerization shrinkage behavior of restorations.
Dental Materials, 2024. Link here |
|
This in vitro study aimed to compare the light-transmission properties of two chairside CAD/CAM lithium disilicate (LD) ceramics (a novel fully crystallized and a traditional pre-crystallized) across varying thicknesses. Light transmittance was significantly affected by ceramic thickness. The 0.5 mm thick specimens exhibited the highest transmittance values compared to all other groups, while a light transmittance of 0.00 was observed in the 2.0 mm thick specimens for both e.max CAD and LiSi GC Block. In the comparison between e.max CAD and LiSi GC Block according to thickness, there was a statistically significant difference exclusively between groups with a thickness of 1.50 mm (p = 0.002). Conclusions: Light transmission for pre- and fully crystallized CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramics only showed a statistical difference at the thickness of 1.50 mm (p = 0.002). E.max CAD demonstrated acceptable light transmission up to a thickness of 1.5 mm. A thickness of 2 mm for chairside CAD/CAM lithium disilicate ceramics, whether pre-crystallized or fully crystallized, necessitates the use of dual-cure resin luting cement due to reduced light transmission.
Materials, 2024. Link here |
|
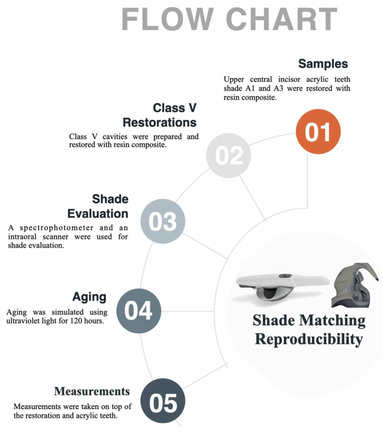
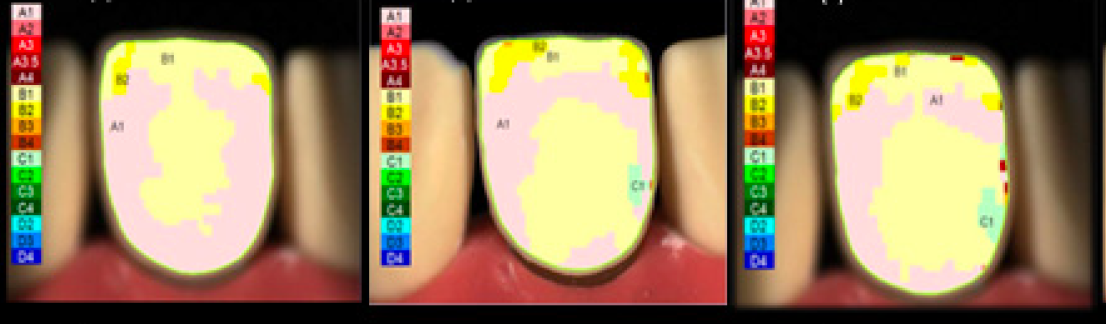
We compared the repeatability of the shade determination of resin composite restorations and acrylic teeth in light and darker shades at baseline and after an aging process through two digital tooth color-matching methods: using a Trios 3Shape intraoral scanner and using a Vita Easyshade Compact spectrophotometer. There was no statistically significant comparison between the shade measurement devices (p > 0.05). At baseline, the repeatability for both the Trios intraoral scanner and the Vita Easyshade Compact device for artificial teeth in the shades A1 and A3 was 100%. After aging, the trueness recorded by the intraoral scanner and the Easyshade device for artificial teeth in the shade A1 was 80%. For Class V restoration with shade A1, the intraoral scanner recorded 80% trueness and the Easyshade device recorded 60% trueness at baseline. For shade A3, the intraoral scanner recorded 60% trueness and the Easyshade device recorded 60% trueness.The intraoral scanner and Easyshade device are reliable for baseline shade selection, but their accuracy decreases after aging, particularly for darker shades.
Dentistry Journal, 2024. Link here |
|
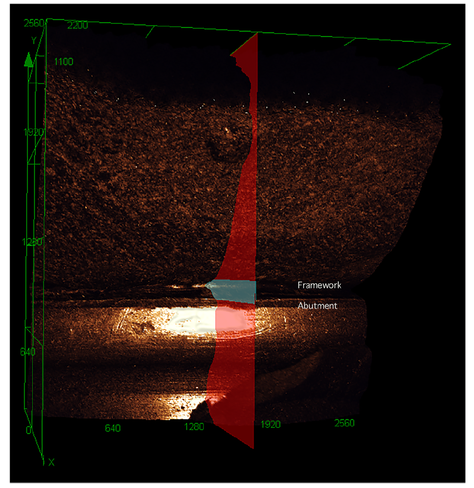
This study aimed to develop and evaluate a simple, non-destructive method for assessing the misfit and passivity of implant-retained prostheses frameworks. To simulate the rehabilitation of a mandible posterior partially edentulous area using 3-unit screw-retained frameworks supported by two implants were fabricated and divided into the following five groups (n = 10 in each group): OP = one-piece framework cast in Co-Cr with the conventional method (control-group); Co-Cr frameworks sectioned and welded by laser (=LAS) or tungsten inert gas (=TIG); Co-Cr CAD-CAM = milled Co-Cr framework; Zir CAD-CAM = milled zirconia framework. The horizontal |X| and vertical |Y| misfits were measured using confocal laser scanning microscopy with one or both screws tightened. The frameworks, whether cast and sectioned with laser welding or milled from Co-Cr, exhibit improved marginal misfit and enhanced passive fit when compared to other fabrication methods. Additionally, the use of confocal laser scanning microscopy is highly effective for passivity and misfit analysis.
Journal of Prosthodontics, 2024. Link here |
|
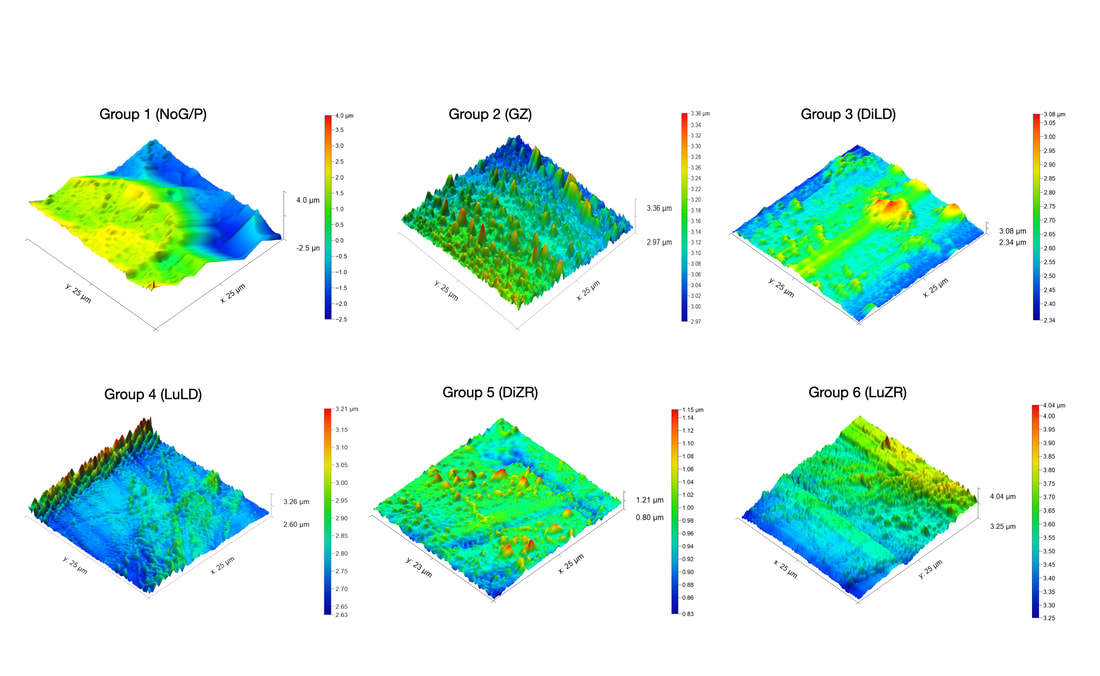
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of glazing, two zirconia, and two lithium disilicate polishing systems on surface roughness of a CAD/CM lithium disilicate and virgilite ceramic with atomic force microscopy (AFM) and visual assessment performed by dental students and faculty. Polishing and glazing considerably improves the surface smoothness of maxillary central incisor crowns fabricated out of a chairside CAD/CAM lithium disilicate and virgilite ceramic. Altogether, zirconia polishing systems provided smoother and more clinically acceptable surface than the lithium disilicate kits.
Operative Dentistry, 2023. Link here |
|
This study aimed to compare the surface finish of milled leucite reinforced ceramics polished with ceramic and composite polishing systems based on the manufacturers’ recommendations. Composite polishing systems did not provide as smooth surfaces as the ceramic polishing kit for CAD-CAM leucite- reinforced ceramics. Thus, using ceramic polishing systems, polishing leucite ceramics is recommended, whereas composite polishing systems should not be considered as an alternative for use in minimally invasive dentistry.
Medicina, 2023. Link here |
|
This in vitro study aimed to evaluate the final shade of translucent zirconia laminate veneers with varying thicknesses over teeth with different shades. The results indicated that the thinner restorations showed higher values with the color imaging spectrophotometer, suggesting that thinner veneers may result in more consistent color matching. This study underscores the importance of carefully considering thickness and background shade when selecting zirconia laminate veneers, to ensure optimal color matching and overall aesthetic outcomes.
Materials, 2023. Link here |
|
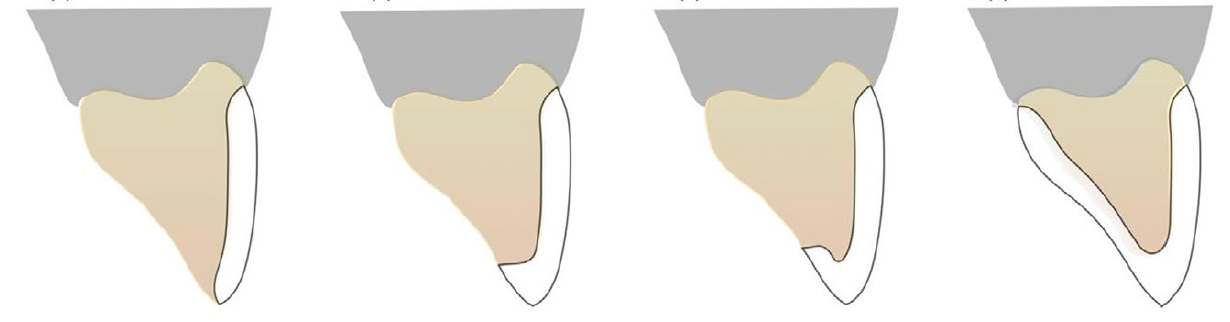
This study aimed to assess the fracture resistance of monolithic zirconia reinforced lithium silicate laminate veneers (LVs) fabricated on various incisal preparation designs. The fracture resistance of chairside milled ZLS veneers was significantly influenced by the incisal preparation designs tested. Within the limitation of this study,
when excessive occlusal forces are expected, LV with palatal chamfer display is the most conservative method of fabricating an indirect restoration. Journal of Prosthodontics, 2023. Link here |
|
The purpose of this study was to assess the effects of water storage on the surface microhardness (VHN) and fracture toughness (K1C) of two self-adhesive restorative materials compared to traditional resin composite and resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) restorative materials. Self-adhesive/ion-releasing resin composites were negatively affected by water storage. Material reinforcements are possible future areas to explore.
Coatings, 2023. Link here |
|
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of traditional and conservative endodontic access hole preparation on fracture resistance of chairside computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) lithium disilicate maxillary right central incisor crowns. Conservative ovoidal endodontic access provides crowns with higher fracture resistance than traditional triangular endodontic access. Crowns with no endodontic access provided the highest resistance than other types of endodontic access.
Journal of Prosthodontics, 2022. Link here |
|
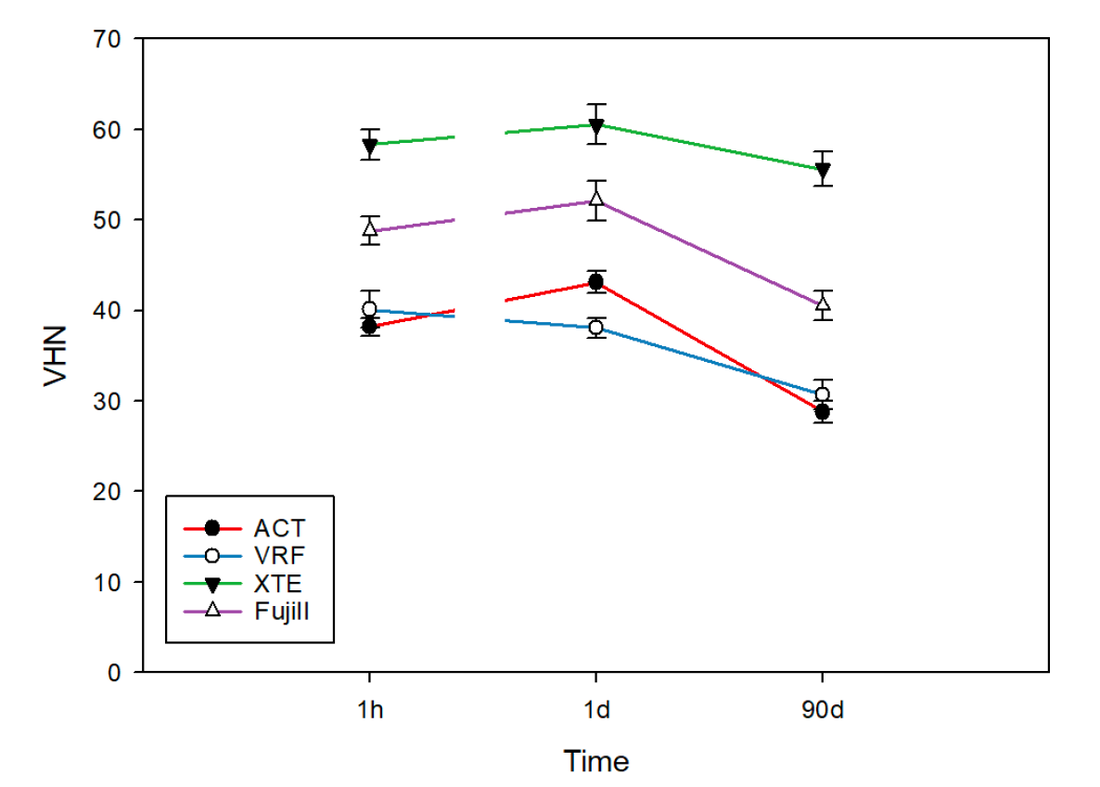
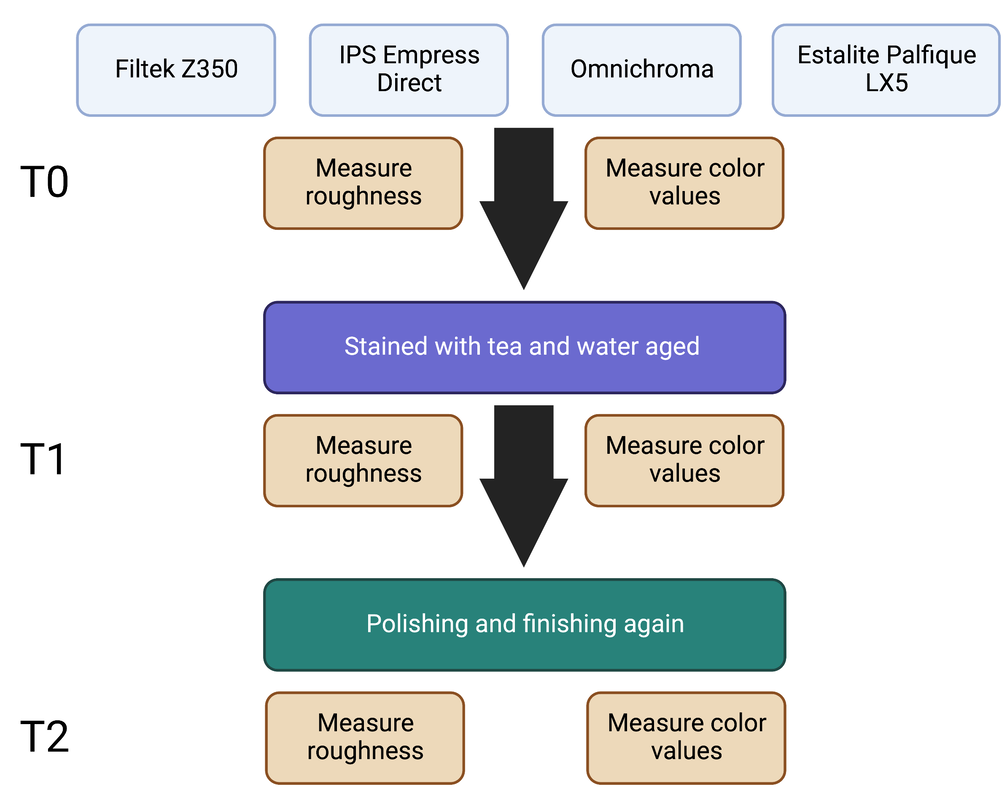
The aim of this in vitro study is to compare the color stability and surface roughness of conventional and self-blending resin composites before and after staining and aging. Three conventional (Filtek Z350, IPS Empress Direct, and Estalite Palfique LX5) and one self-blending (Omnichroma) resin composites were used in this study. All groups showed significant decrease in all color parameters (L*, a*, and b*), however, after polishing, all groups showed color enhancement matching pre-experiment baseline color in all color parameters (L*, a*, and b*) except for Estelite Palfique LX5 which showed a significant difference in L relative to baseline. Furthermore, Estalite Palfique LX5 showed increased roughness after staining compared to baseline, unlike other groups. No significant differences in color stability were found between self-blending composite and other composite materials. Accelerated aging and staining had minimal effects on surface roughness of self-blending composite.
Biomimetics, 2022. Link here |
|
The purpose of this study is to compare bond durability, in terms of fatigue bond strength, of a two-step HEMA-free universal adhesive and representative adhesives in each systematic category. The adhesives used in this study were OptiBond FL, Prime&Bond NT, Clearfil SE Bond 2, G2-BOND Universal, and Scotchbond Universal Plus Adhesive. The two-step HEMA-free universal adhesive showed higher enamel and higher or equal dentin fatigue bond strength than other selected representative adhesive systems in etch-and-rinse mode and higher or equal enamel and higher dentin fatigue bond strength than adhesive systems in self-etch mode.
Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 2022. Link here |
|
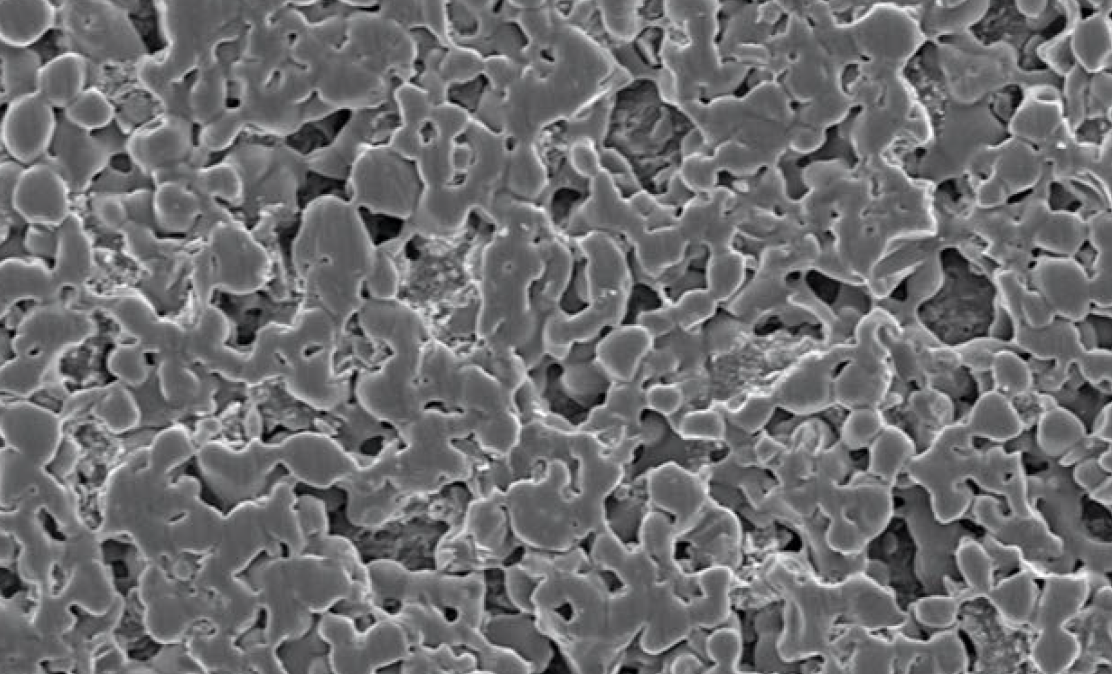
This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of two ceramic and two composite polishing systems for a novel chairside Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) lithium disilicate ceramic with 3-dimensional and 2-dimensional microscopy images. This ceramic material can be used for implant-supported or tooth-borne single-unit prostheses. Despite the effectiveness of ceramic polishing systems being superior to composite polishing systems of the CAD/CAM lithium disilicate restorative material, both polishing systems significantly improved the smoothness.
Materials, 2022. Link here |
|
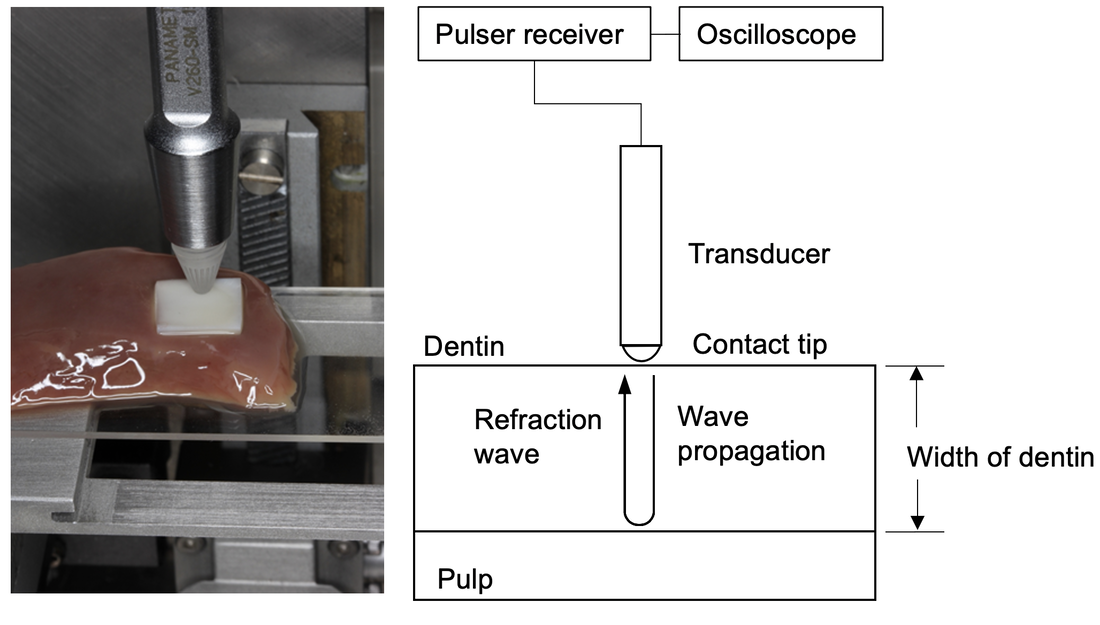
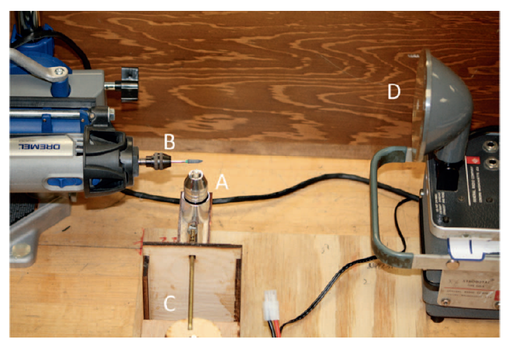
This study investigated the ability of a pencil-type transducer connected to a pulser-receiver to measure remaining dentin thickness (RDT). The agreement between different measurement methods was analyzed to evaluate the inter-methodology variation. The Bland–Altman comparison method revealed a mean difference of 0.0098 ± 0.724 mm between the ultrasonic technique and the direct measurement, with the 95% Bland–Altman limits of agreement ranging from −0.1322 to 0.1517 mm. Ultrasonic measurement using the pencil-type transducer might be a promising method to evaluate remaining dentin thickness.
American Journal of Dentistry, 2021. Link here |
|
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of five different polishing systems on a CAD/CAM polymer-infiltrated ceramic network restoration with nanoscale assessment using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and visual assessment performed by dental school senior students and faculty members. Ceramic and composite polishing systems produced similar polishing results as that observed using a company proprietary polishing system. However, effectiveness for polishing using a company proprietary and ceramic polishing system tend to be higher than composite polishing systems.
Operative Dentistry, 2021. Link here |
|
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the influence of 38% silver diamine fluoride (SDF) on enamel and dentin bonding (static and fatigue) using three universal adhesives in self-etch mode.
Conclusion: Despite the conflicting results in the literature, our results suggest that SDF applications on enamel and dentin surfaces reduces the bond fatigue durability of bonded resin composite using universal adhesives in self-etch mode European Journal of Oral Sciences, 2020. Link here |
|
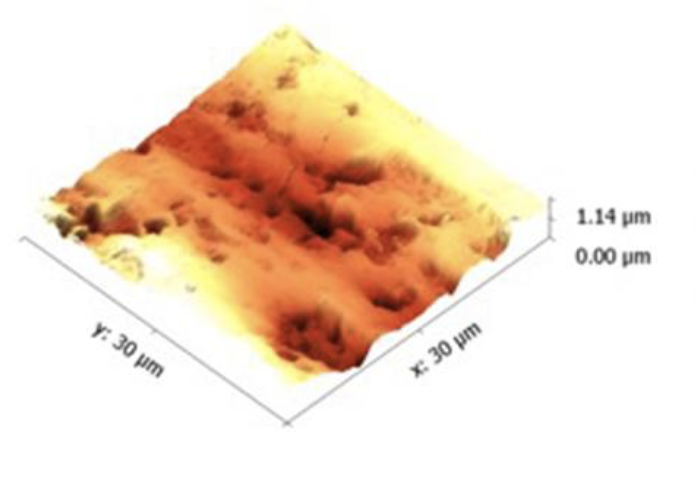
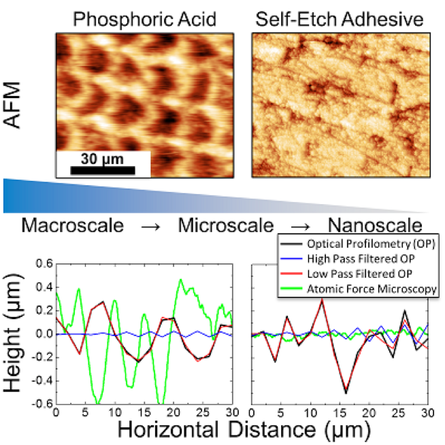
Purpose: 1) evaluate the role of enamel surface roughness on bond fatigue durability and 2) evaluate statistical differences in roughness values based on measurement technique, including the use of spatial filtering for optical profilometry.
Conclusion: Roughness values showed differences based on measurement technique and strong correlations with bond and fatigue strength. The filtered op group demonstrated the importance of careful usage and reporting of atomic force microscopy and optical profilometry metrics in adhesive dentistry. Best practices for surface roughness analysis were also discussed. Microscopy Research and Technique, 2019. Link here |
|
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether different enamel etching methods with reduced etching times would improve the bonding effectiveness of universal adhesives.
Conclusion: Phosphoric acid etching for <1 s to 15 seconds, and polyalkenoic acid etching for 15 seconds improve universal adhesive bonding, surface Ra roughness and surface area of enamel. However, phosphoric acid ester monomer etching is not effective, regardless of etching time, in improving bonds strengths, increasing surface roughness or increasing surface area. Operative Dentistry, 2019. Link here |
|
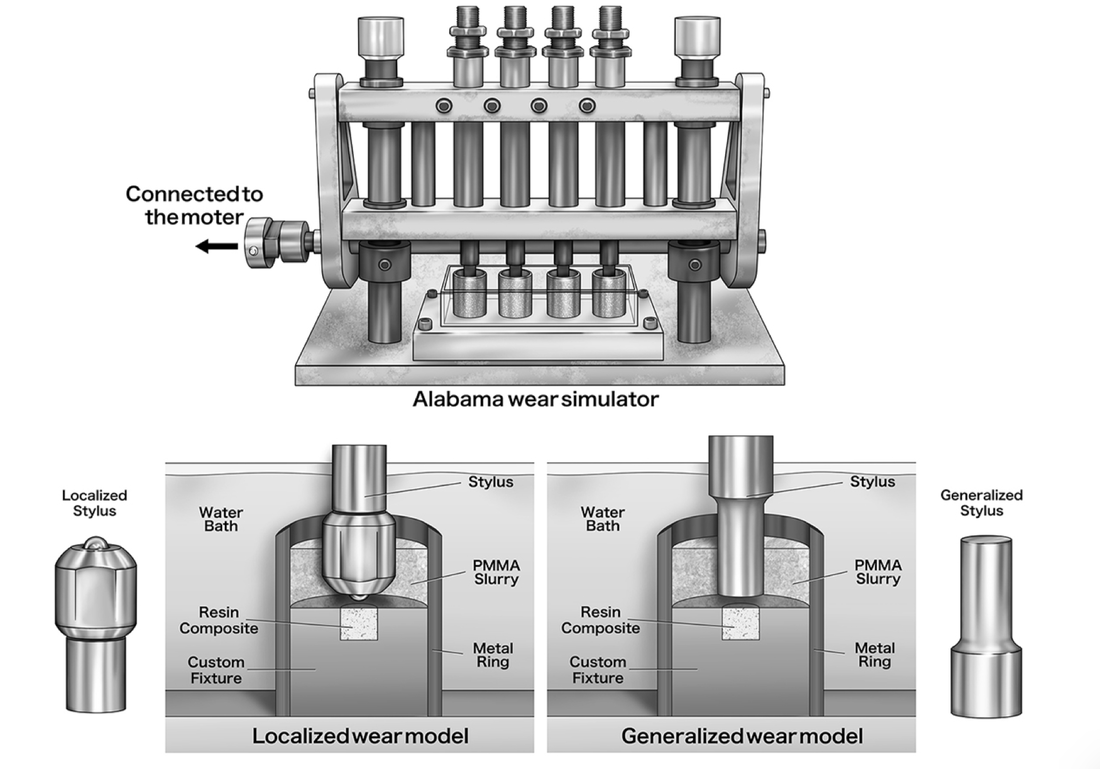
Purpose: The aim of this laboratory study was to investigate simulated localized and generalized wear of indirect resin composites used for implant supported provisional restorations.
Conclusion: Although only some indirect resin composites showed similar wear resistance to CAD/CAM resin composites, the wear of all the indirect resin composites was lower than that of bis-acryl base provisional resin and polymethyl methacrylate resins. Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics, 2019. Link here |
|
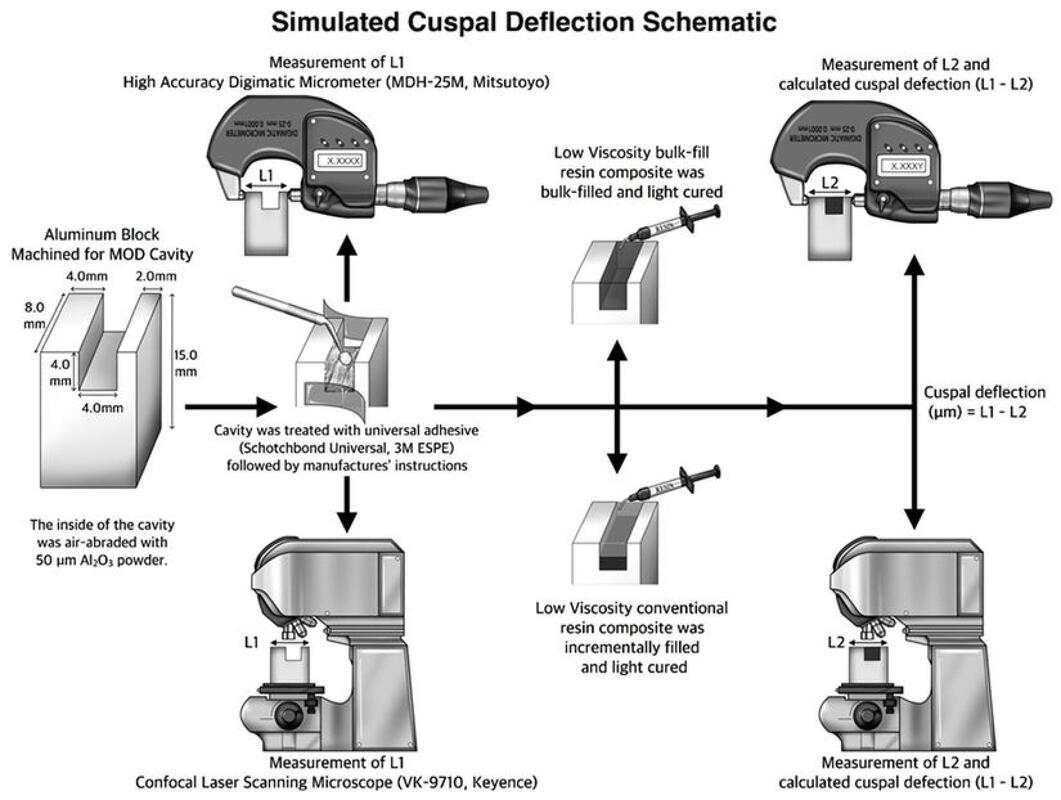
Purpose: This study investigates simulated cuspal deflection and flexural properties of low viscosity bulk fill and conventional flowable resin composites.
Conclusion: These results indicate that some low viscosity bulk-fill resin composites exhibit lower cuspal deflection with the bulk-filling technique than is shown by conventional flowable resin composites using the incremental filling technique. Simulated cuspal deflection can be measured using either a micrometre or clsm, but this experiment failed to show a relationship between cuspal deflection and flexural properties of resin composites. Operative Dentistry, 2019. Link here |
|
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether surface moisture would influence the bonding effectiveness of universal adhesives in etch-and-rinse mode.
Conclusion: Some universal adhesives with the addition of specific components and optimization of water content can achieve stable bonds regardless of surface moisture, but the surface moisture of dentin, but not enamel, is still a significant factor for universal adhesive bonding in etch-and rinse mode. American Journal of Dentistry, 2019. Link here |
|
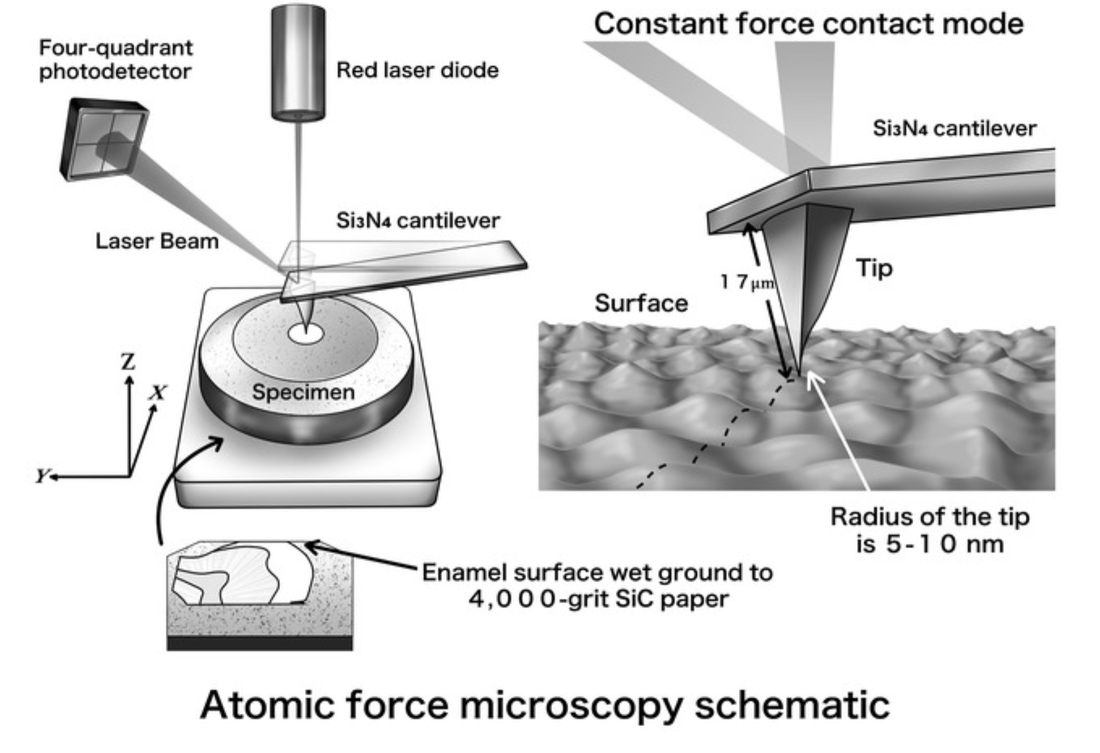
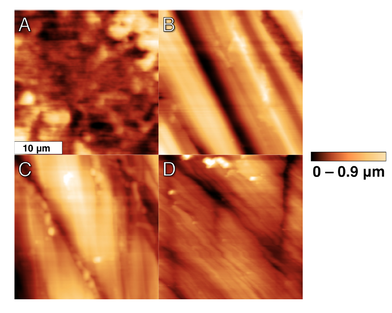
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of reduced application times of universal adhesives on enamel bond fatigue and surface morphology of the treated enamel with constant force atomic force microscopy (AFM).
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that universal adhesives, used with reduced application times, have adequate Ra surface roughness to provide sufficient resistance to enamel bond fatigue at application times from <1 second to 20 seconds, while the geometric surface area of adhesive-treated enamel did not show any significant changes at these different application times. Operative Dentistry, 2019. Link here |
|
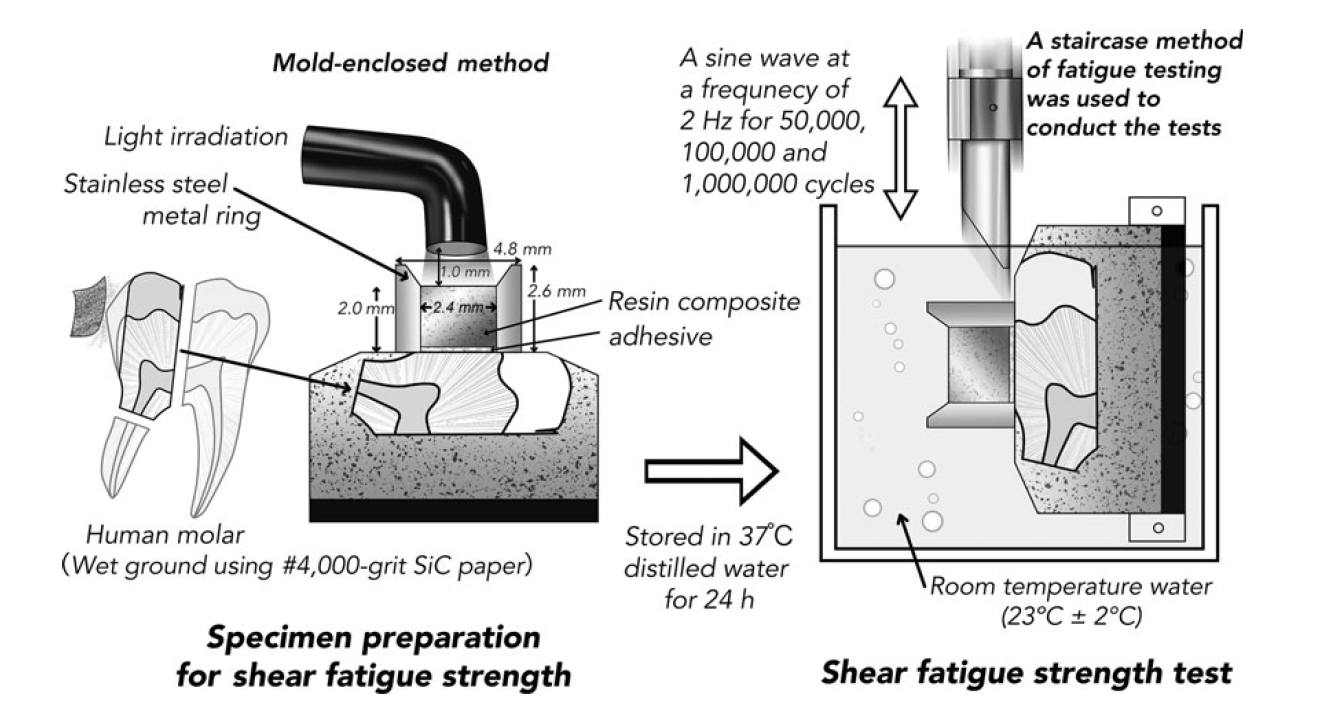
The purpose of this study was to examine the shear fatigue strengths of a resin composite bonded to dentin. Three adhesive systems – a two-step self-etch adhesive (OptiBond XTR; Kerr) and two universal adhesives [Scotchbond Universal (3M ESPE) and G-Premio Bond (GC)] – were used in self-etch mode to bond a resin composite to dentin at a physiologic frequency of 2 Hz over 50,000, 100,000, and 1,000,000 cycles. A staircase method of fatigue testing was used. Twenty specimens were used for each test condition. There was no significant difference in shear fatigue strength across the cycling periods for the three individual adhesives. Differences in shear fatigue strength were found among the three adhesives within each cycling period. Regardless of the adhesive used in self-etch mode for bonding a resin composite to dentin, shear fatigue strength was not influenced by the number of cycles used for testing.
European Journal of Oral Sciences, 2018. Link here |
|
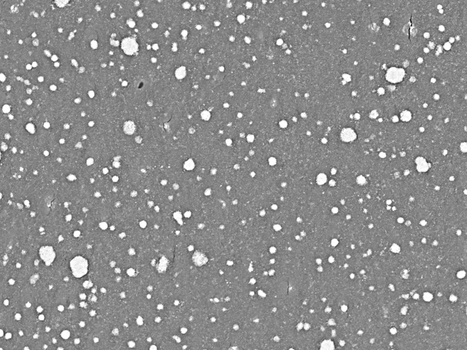
Purpose: Limited information is available on how to polish and finish zirconia surfaces following computer-aided design/computer aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM), specifically, how differing application forces and reuse of zirconia polishing systems affect zirconia topography. Our purpose was to determine the effect of differing, clinically relevant, polishing application forces and multiple usages of polishing burs on the surface topography of CAD/CAM zirconia.
Conclusion: These in vitro results suggest changes in OP Ra due to bur reuse and polishing application force. Within the parameter of this study, the resultant topography of zirconia polishing is force-dependent and the reuse of coarse polishing burs is possible without statistically significant differences in Ra values after initial use. Nanoscale and microscale topography were shown to depend on specific polishing bur type. Operative Dentistry, 2018. Link here |
|
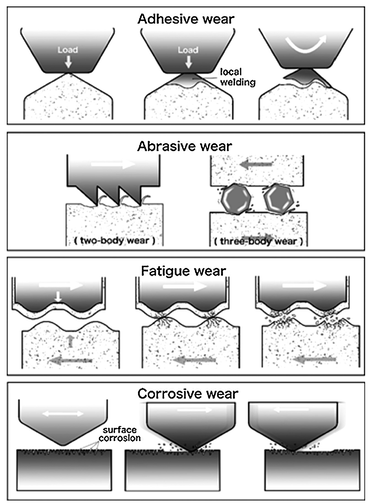
The application of resin composites in dentistry has become increasingly widespread due to the increased aesthetic demands of patients, improvements in the for-mulation of resin composites, and the ability of these materials to bond to tooth structures, together with concerns about dental amalgam fillings. As resistance to wear is an important factor in determining the clinical success of resin composite restoratives, this review article defines what constitutes wear and describes the major underlying phenomena involved in this process. Insights are further included on both in vivo and in vitro tests used to determine thewear resistance of resin composite and the relationships between these tests. The discussion focuses on factors that contribute to the wear of resin composite. Finally, future perspective sare included on both clinical and laboratory tests and on the development of resin composite restorations.
Japanese Dental Science Review, 2018. Link here |
|
Mucosal seal formation around dental abutments is critical to the successful integration of dental implants into the human oral cavity. No information exists for how clinically relevant polishing procedures for computer-aided design and computer-aided manufactured (CAD/CAM) zirconia abutments affects cellular responses important to mucosal seal formation.
Materials, 2017. Link here |
|
Purpose: To examine the effect of reduced phosphoric acid pre-etching times on enamel fatigue bond strength of universal adhesives and surface characteristics by using atomic force microscopy (AFM).
Conclusions: The results of this in vitro study suggest that reduced phosphoric acid pre-etching times do not impair the fatigue bond strength of universal adhesives. Although fatigue bond strength and surface area were not influenced by phosphoric- acid etching times, surface roughness increased with increasing etching time. Journal of Adhesive Dentistry, 2017. Link here |