|
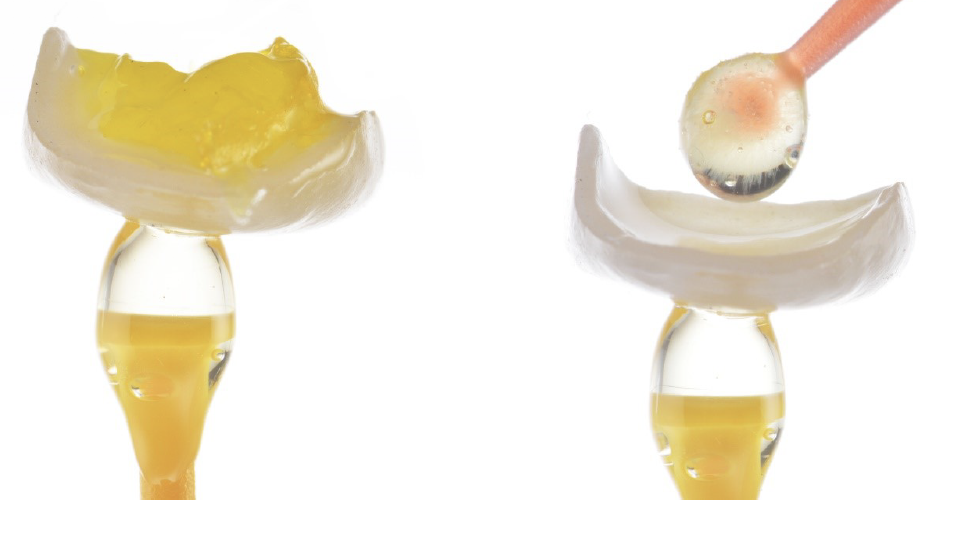
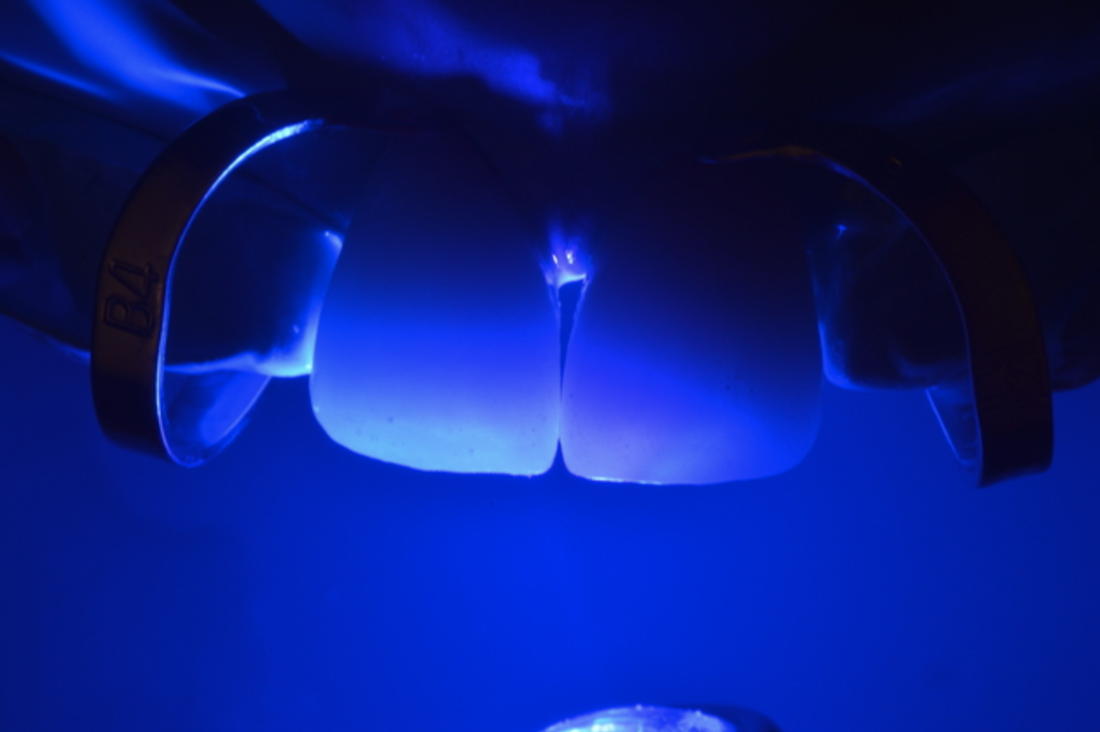
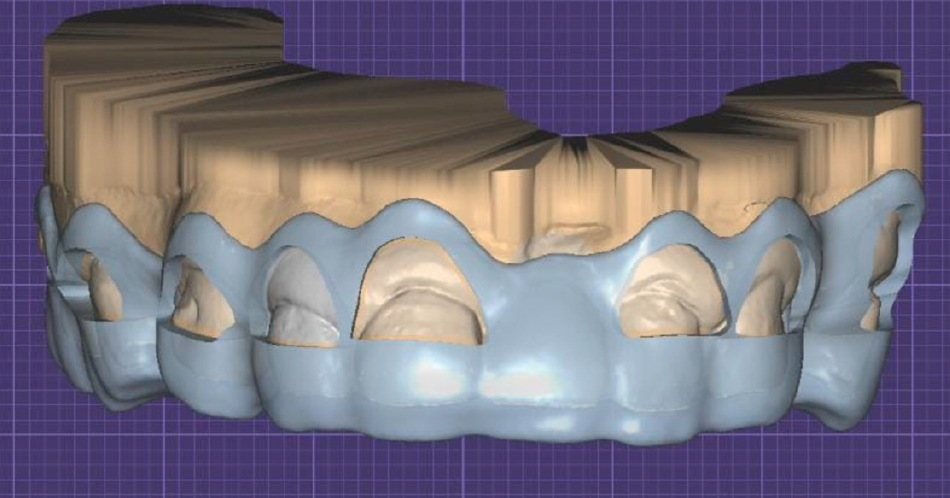
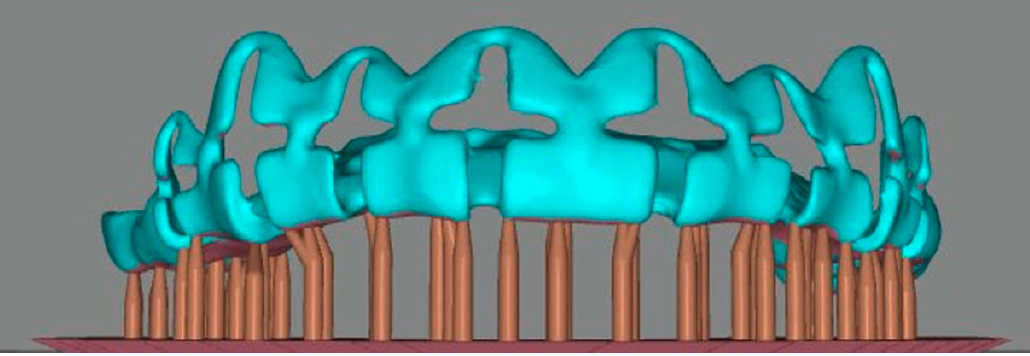
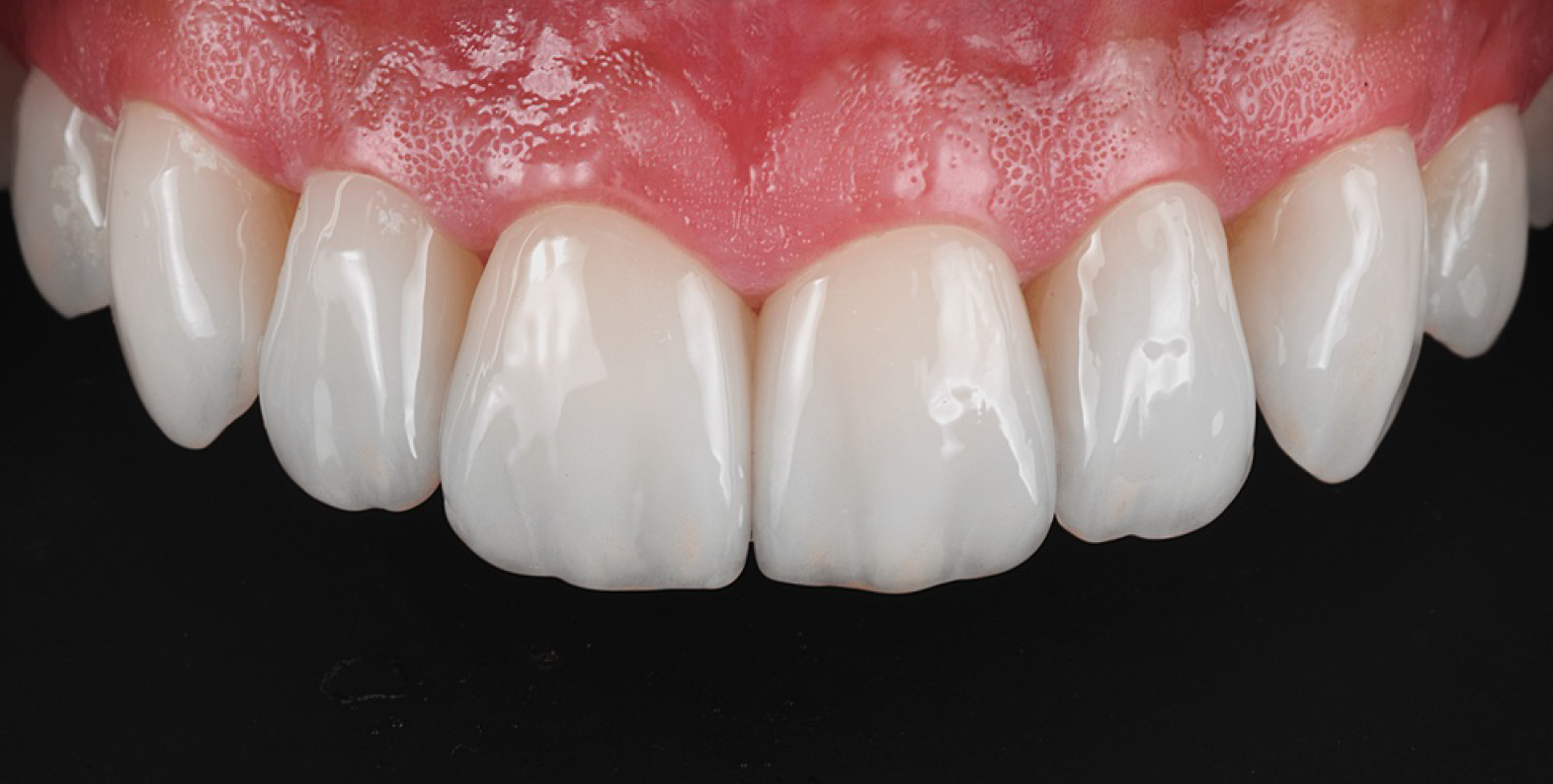
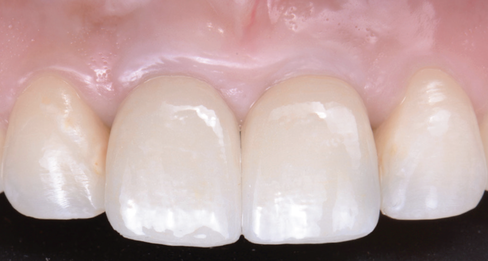
This report describes a technique integrating facial and dental scanners for treatment planning and execution of a tooth-borne full-mouth reconstruction (FMR) with zirconia fixed prostheses. An intraoral scan (IoS) for both arches and facial scans collected the initial clinical situation. A digital diagnostic wax-up was generated as part of the treatment plan, and the models were printed. The intervention included crown lengthening of the maxillary teeth aided by a printed guide, installing milled provisional restorations, and delivering permanent milled zirconia partialrestorations, single crowns (SCs), and fixed dental prostheses (FDPs). The functional extraoral scanner permitted designing an FMR that created a harmonious dental, gingival, and facial relationship with the patient’s esthetic consent approval. IoS captured the initial clinical situation to design (CAD) and fabricate (CAM) the PMMA provisional and zirconia final partial restorations, SCs, and FDPs.
Applied Sciences, 2023. Link here |
|
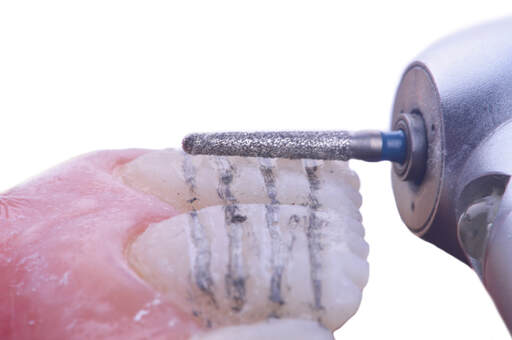
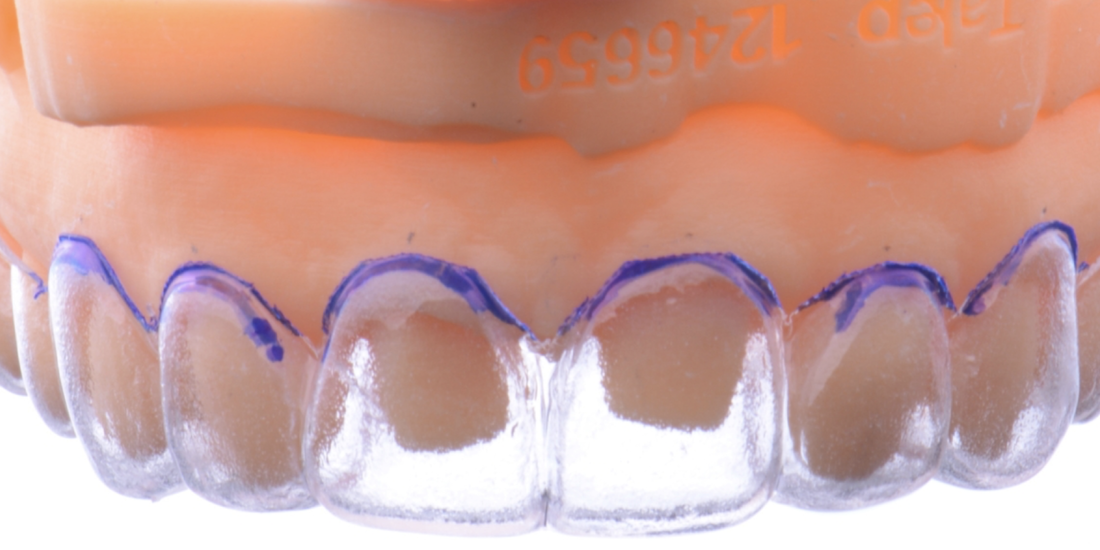
This case report describes a novel design (CAD) for an additive computer-aided manufactured (a-CAM) tooth reduction guide with channels that permitted access for the preparation and evaluation of the reduction with the same guide. The guide features innovative vertical and horizontal channels that permit comprehensive access for preparation and evaluation of the reduction with a periodontal probe, ensuring uniformtooth reduction and avoiding overpreparation. This approach was successfully applied to a female patient with non carious lesions and white spot lesions, resulting in minimally invasive tooth preparations and hand-crafted laminate veneer restorations that met the patient’s aesthetic demands while preserving tooth structure.
Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 2023. Link here |
|
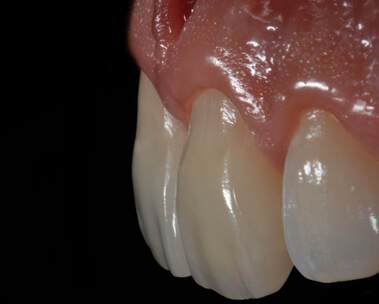
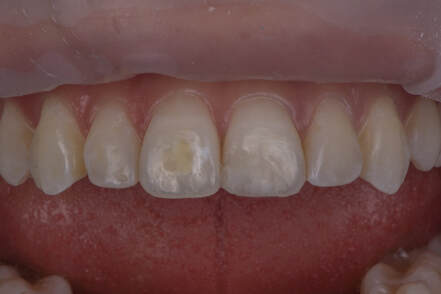
This clinical report describes the combination of minimally invasive and non-preparation ceramic laminate veneers in the esthetic zone with a 6 year follow-up to replace stained resin composite veneers on both maxillary central incisors. The 6 year follow up showed stained composite veneers can successfully be replaced with minimally invasive and non-prepared ceramic veneers to fulfill the patient’s esthetics concerns. Overall, well-planned and executed restorative procedures combining minimal preparation and non-preparations for ceramic laminate veneers can achieve esthetically pleasing outcomes and maximize tooth structure preservation in the maxillary anterior region.
International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry, 2023. Link here |
|
Partial veneers and whitening are a conservative treatment option for restoring chipped direct restorations in the esthetic zone. Here, we show minimal tooth preparation paired with partial ceramic veneers and whitening without degradation of the esthetic outcomes at a 5 year follow-up.
Operative Dentistry, 2023. Link here |
|
This report describes the importance of and outlines steps for additive wax-up and diagnostic mockup for anterior teeth as diagnostic and driving tools for non-prep and minimally invasive veneer preparations. Overall, additive wax-up provides information needed to know if minimally invasive veneer preparations are possible, and the diagnostic mockup displays a physical, tentative outcome for the patient’s evaluation before irreversible tooth preparations. These simple, but effective, techniques can drive the diagnosis and prognosis of minimally invasive veneer restorations.
Cureus, 2022. Link here |
|
There is concern that differences in the compositions of materials used to simultaneously treat existing resin composites and dental fluorosis may negatively affect the esthetic quality over time. This report shows a technique in which no esthetic deterioration is observed over five years.
Operative Dentistry, 2022. Link here |
|
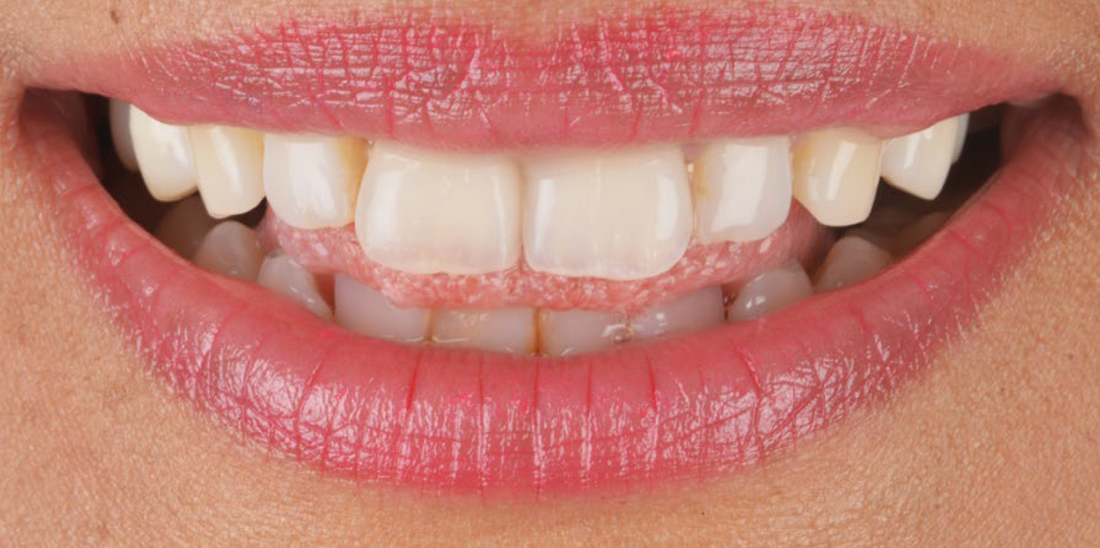
This report describes a minimally invasive multidisciplinary approach to a single discolored anterior tooth, with internal bleaching using traditional Japanese paper (washi), a gingivectomy with a 3-dimensional (3D) printed surgical guide, and ultra-thin ceramic veneers. After clinical evaluation, internal tooth bleaching for the discolored tooth, and gingivectomy with restorations of the maxillary anterior six front teeth and first premolars were recommended. Once the tooth bleaching was completed, the 3D printed surgical guide was placed in the patient’s maxillary anterior region and used to guide the soft tissue re-contouring. After six months, ultra-thin feldspathic porcelain veneers were provided.
Operative Dentistry, 2021. Link here |
|
The combination of partial edentulism and a worn anterior tooth in the esthetic zone can be a challenge for the dentist. This clinical situation requires extensive knowledge of soft and hard tissue management, surgical planning and execution for implant therapy, and conservative tooth preparation with ideal bonding protocols for the tooth-supported prosthesis. Moreover, an optimal selection of the final restorative materials is imperative to manage occlusal forces and fulfill the patient’s esthetic demands.
International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry, 2020. Link here |
|
This case report demonstrates a method for feldspathic veneers with diagnostic wax-ups, subsequent mock-up, and reduction guides and how these can lead to good patient esthetics at a 5-year follow up. This case report shows a 5-year follow-up of feldspathic veneer restorations for a patient with excessive space between teeth, defective composite restorations on facial and incisal surfaces, and worn teeth. Veneers were delivered with conservative tooth preparation combining different tooth reduction guides.
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, 2021. Link here |
|
The in-office whitening agent (Opalesence Boost 35%) was used in this study. Two whitening regimens were evaluated on maxillary anterior teeth: 1) with light irradiation; and 2) without light irradiation. The ΔE*, changes of L*, a*, b*, and the best shade match on the central incisor before, immediately after, and 6-month after whitening procedures were evaluated using a dental spectrometer. The results of this study suggested that the in-office whitening agent using 35% hydrogen peroxide without photo catalysts can improve tooth color with or without light irradiation for 6 months after whitening.
American Journal of Dentistry, 2021. Link here |
|
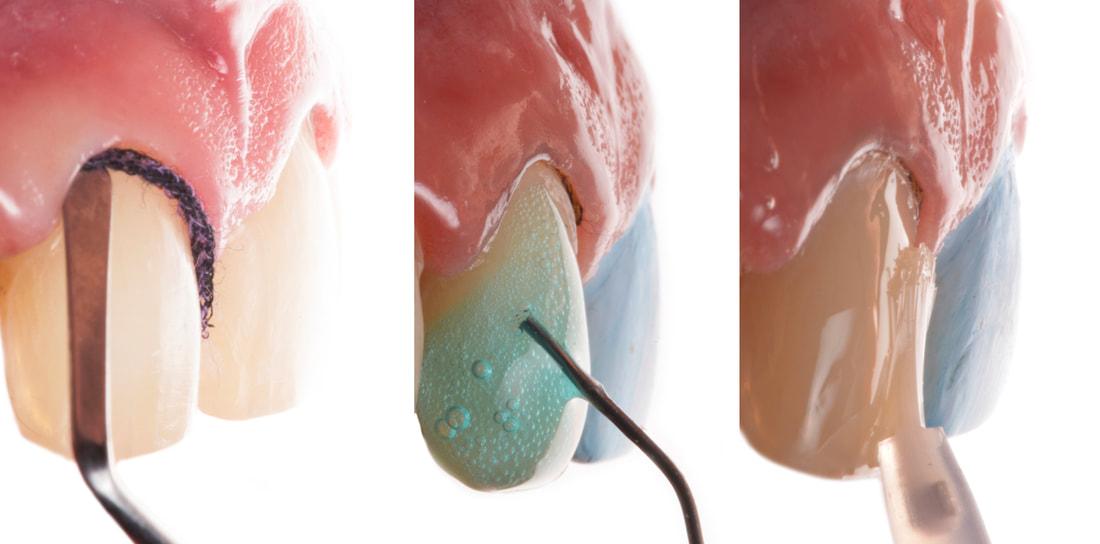
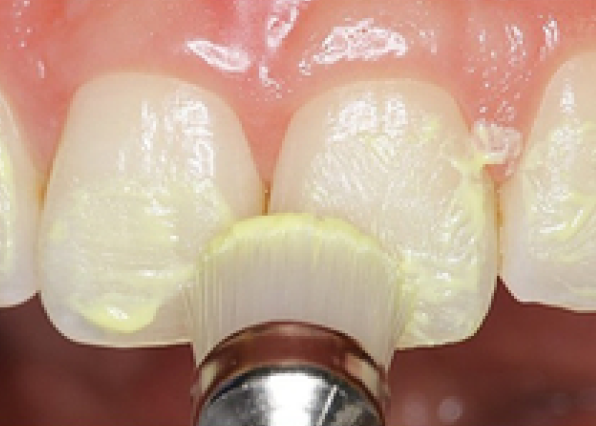
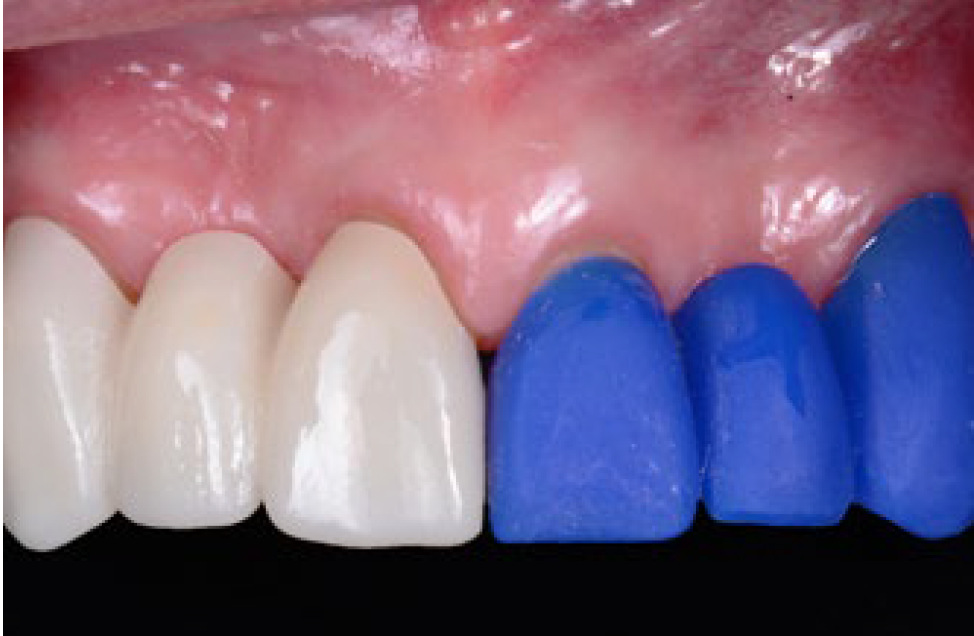
It has been well documented that uncontaminated ground enamel provides the most predictable substrate for the bonding of ceramic veneers, and thus conservative tooth preparation with complete isolation using a rubber dam are key to the success of the restorations. Rubber dam isolation provides several advantages to the clinician, such as preventing contamination of the working field by saliva, blood and sulcular fluids, and improving direct visibility. However, it may be a challenge to the younger clinician to properly isolate teeth prior to bonding ceramic veneers. The present article demonstrates the sequence and some clinical tips for a case in which the rubber dam is placed from one second premolar to the opposite second premolar and held with clamps, the rubber dam is gently invaginated into the sulcus, and clamps are selected and placed on each tooth to create an ideal situation for the adhesion of the ceramic veneer.
Cureus, 2021. Link here |
|
Hypodontia is a common developmental problem of human dentition. The treatment of missing maxillary central incisors is always a challenging task, often requiring a multidisciplinary approach. Critical analysis of the treatment plan through cooperation among specialists is required to obtain the ideal result. Orthodontic treatment may be necessary to close or gain more space, followed by implant placement and restorative treatment. It is important to create the treatment plan through a multidisciplinary approach involving orthodontists, surgeons, and restorative specialists before initiating treatment, This case report describes such a multidisciplinary approach for a female patient with congenitally missing maxillary central incisors and class II division 1 occlusion.
Cureus, 2022. Link here |
|
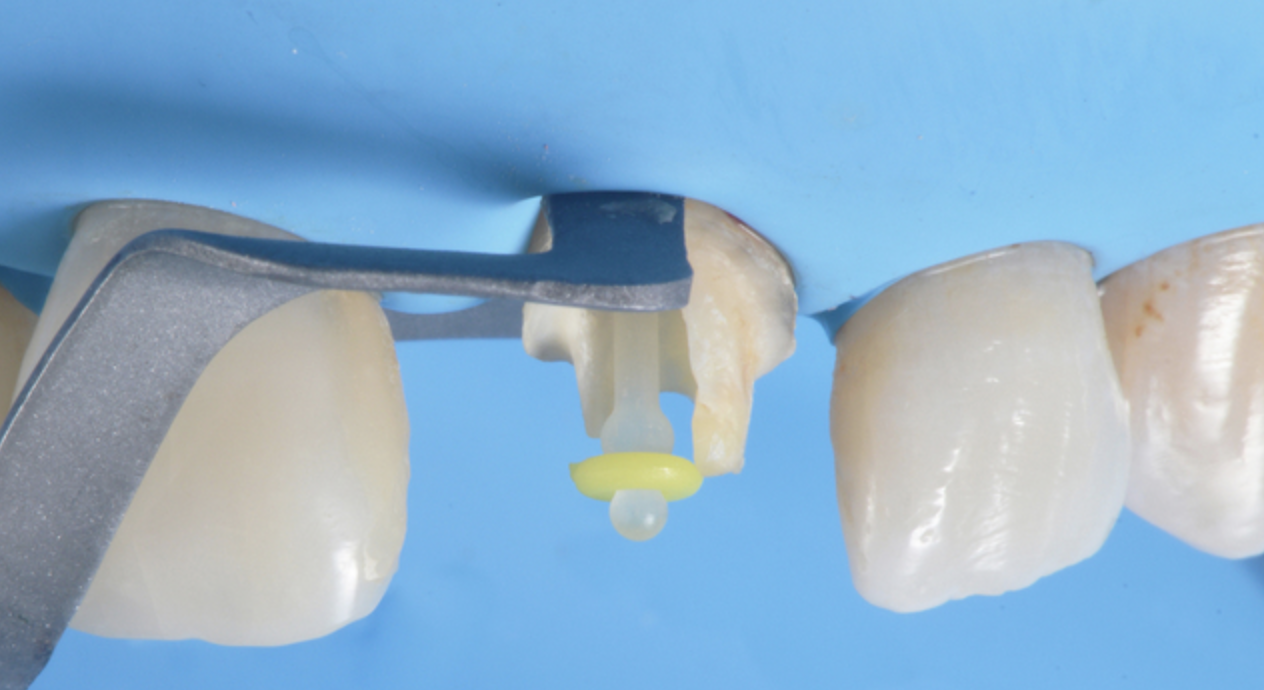
Post and core fabrication are key factors in the restoration of endodontically treated teeth. Teeth with endodontic treatment have commonly experienced significant coronal and radicular dentin destruction, thus preserving all the remaining tooth structure is imperative to improve the prognosis of the restorative treatment. Core height and width need to be carefully designed and built in order to receive the final restoration. Direct free-hand resin composite core build-up in increments may be a challenging and time consuming procedure. This case report describes a clinical technique using a clear matrix to receive injections of a low viscosity bulk-fill resin composite in order to achieve an ideal shape and core size.
International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry, 2020. Link here |
|
The clinical report describes a three-dimensional (3D) printed coping for intraoral evaluation before milling final anterior restorations. The use of printed copings allows restorations for complex and esthetically important restorations to be thoroughly tested at relatively low cost without introducing large delays into the fabrication process
Quintessence International, 2019. Link here |
|
Esthetic rehabilitation of a maxillary central incisor using a dental implant can be a challenging task. The hard and soft tissues must be managed in a way that minimizes the risk of tissue loss, while preserving and/or regenerating full interdental papillae. In addition, advances in restorative materials for implants have led to the introduction of translucent zirconia that can be synergistically combined with zirconia custom abutments. This case report describes implant therapy with monolithic translucent zirconia restorations in the esthetic zone. In this implant therapy, an adequate pink esthetics can be achieved by delayed titanium implant placement with guided bond regeneration. Monolithic translucent zirconia restorations with zirconia custom abutments provide predictable esthetic results.
General Dentistry, 2019. Link here |